Market Risk Management
This field of risk management deals with managing the potential loss in investments as a result of changes in one or more of the macroeconomic factors. Market risk is the risk that cannot be controlled by an institution and it affects the economy as a whole. Changes in macroeconomic and political factors have an influence on the operations and profitability of almost every firm in an economy. It is important to manage this form of risk as it can lead to substantial losses. According to Woods et al., (2008) Risk management is concerned with understanding and managing the risks that an organization faces in its attempt to achieve its objectives. These risks have the effect of losses on the firm.
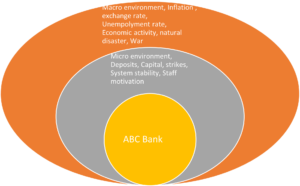
The above diagram illustrates the micro and macro sources of risk available to ABC bank. The micro factors affect only the ABC bank, whereas the macro factors affect the whole economy and the bank cannot control it.
Categories of risk
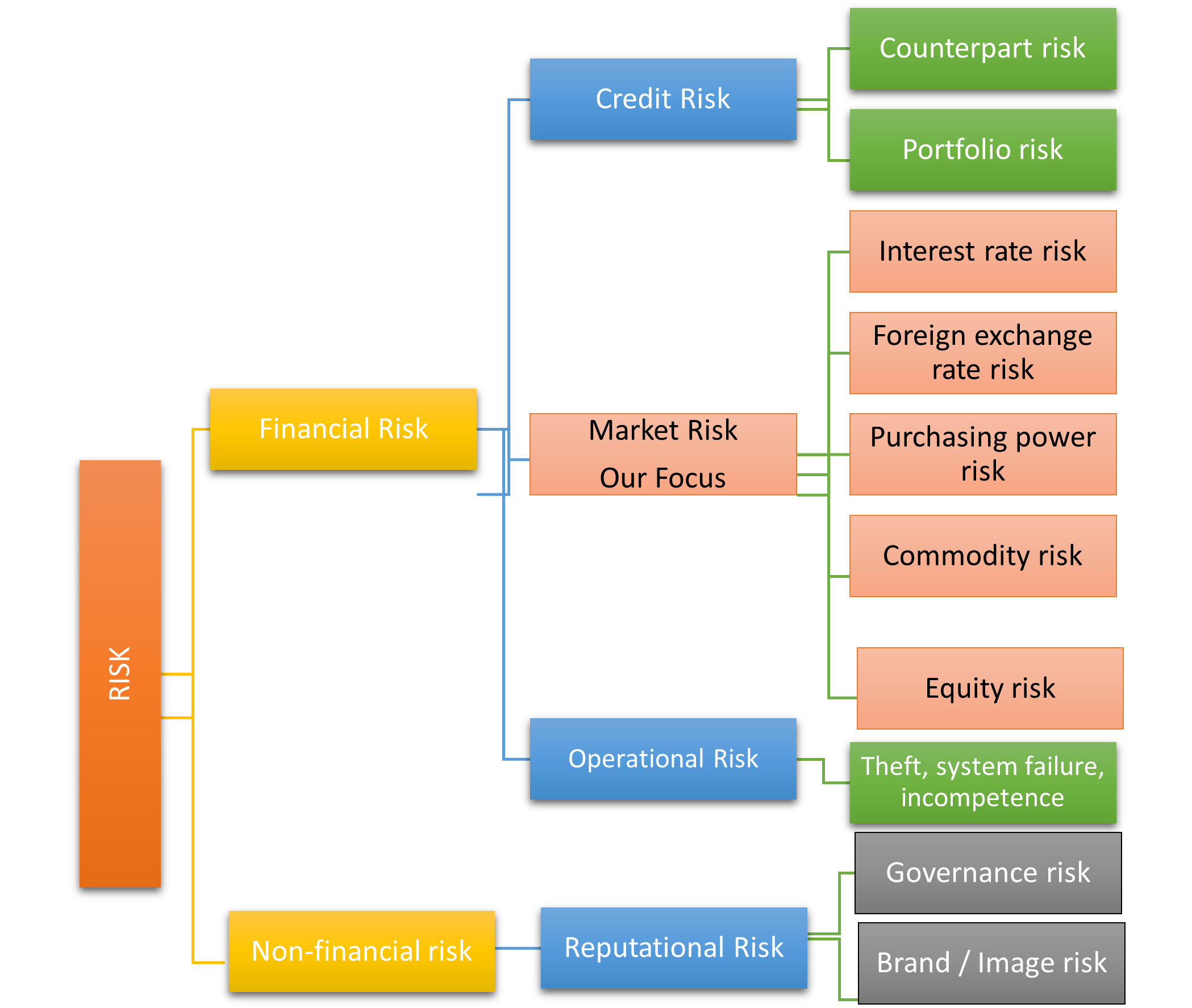
The above diagram explains risk in a broad category. It is vital to take note that this list is not exhaustive and might be presented differently depending on the direction in which the presenter is looking. The operational risk we have presented it under financial risk but it can also be viewed as a non-financial risk. Operational risk may encompass theft, system failures and incompetence among staff, this has the effect of cascading into affecting the financing position of a company. Consider an accident at work it will eventually fork out money to compensate for the affected employees or third parties.
Financial risk
Horcher (2005) pointed out that financial risk arises from numerous transactions, which include sales, purchases, investments and loans. Financial risk is therefore a broad category that includes all market risk, credit risk and liquidity risk.
According to Horcher (2005), the following are the three main sources of risk
- Exposures to market price fluctuations. (Market or systematic risk)
- Financial risk resulting from the trading partners and counterparties.
- Financial risk arising from internal processes, system failures and organisational structure.
Credit Risk
According to Rose and Hudgins (2012), Credit risk is the probability that some of a financial institution’s assets, especially its loans, will decline in value and perhaps become worthless. Banks are more susceptible to credit risk due to their product portfolio. When borrowers fail to honour up their dues the bank will assume the risk associated with non-performing loans. Non-performing loans involve loans in which the customer defaulted and the bank has lost part or both the principal and interest payments.
South Africa Non-Performing Loans (2010 to 2019)
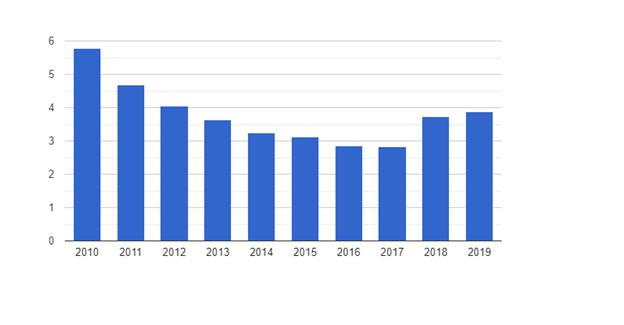
It is important for banking institutions to improve their credit or lending policies to reduce the risk of attracting bad debts. Further reading: (“SA banks are reporting a bad-debt bloodbath – but it may look worse than it really is,” n.d.).
Reputational risk
Rose and Hudgins (2012), Defined reputational risk as negative publicity, whether true or not, that can affect a financial firm’s income by discouraging customers from using the services of the institution, just as positive publicity may serve to promote a financial firm’s services and products. This has the effect of affecting the reputation of the company. Read the case of Ford, South Africa (Theron-Wepener, n.d.) and (“Top Ten Reputational Crises – The 2012 Edition,” 2012)
Bibliography
- Ahmed, S.N.& F., n.d. Risk Management Framework for Indian Banks.
- Horcher, K.A., 2005. Essentials of Financial Risk Management: Horcher/Essentials. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118386392
- Rose, P., Hudgins, S., 2012. Bank Management & Financial Services. Finance Faculty Books.
- South Africa Non-performing loans – data, chart [WWW Document], n.d. The Global Economy.com. URL https://www.theglobaleconomy.com/South-Africa/nonperforming_loans/ (accessed 3.4.21).
- SA banks are reporting a bad-debt bloodbath – but it may look worse than it really is [WWW Document], n.d. . BusinessInsider. URL https://www.businessinsider.co.za/coronavirus-bad-debts-impact-on-the-banks-2020-8 (accessed 3.4.21).
- Theron-Wepener, M., n.d. Ford South Africa failed to protect its reputation. What it should have done [WWW Document]. The Conversation. URL http://the conversation.com/ford-south-africa-failed-to-protect-its-reputation-what-it-should-have-done-71892 (accessed 3.3.21).
- Woods, M., Dowd, K., American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, Society of Management Accountants of Canada, 2008. Financial risk management accountants. CMA Canada, Mississauga, Ont.
